Welcome to the era of Hypergamble Capitalism.
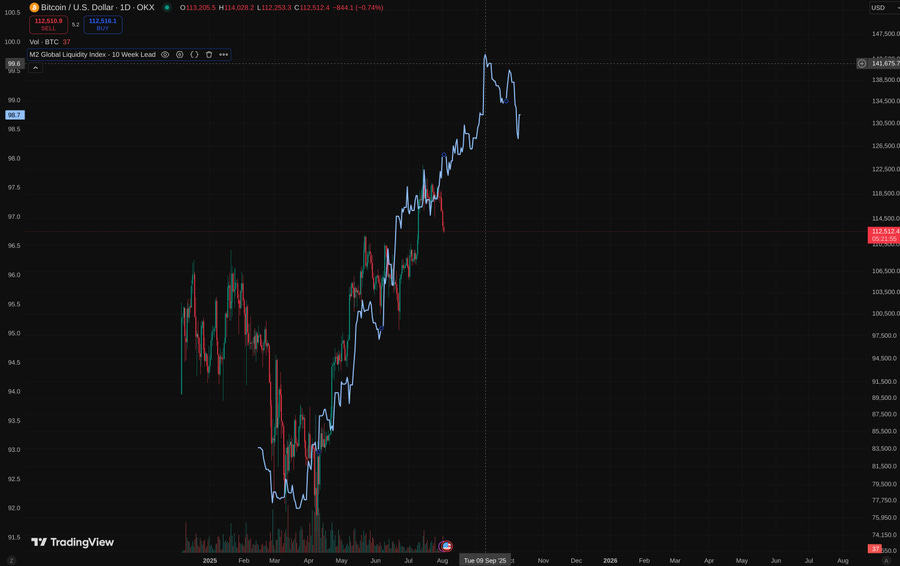
Watch mid-September. Track M2.
Hyper speculation is now a rational reaction to irrational conditions.
Fiscal and monetary policy used to anchor markets in some semblance of reality. That tether is now frayed:
The U.S. is running a 7% GDP deficit—during full employment.
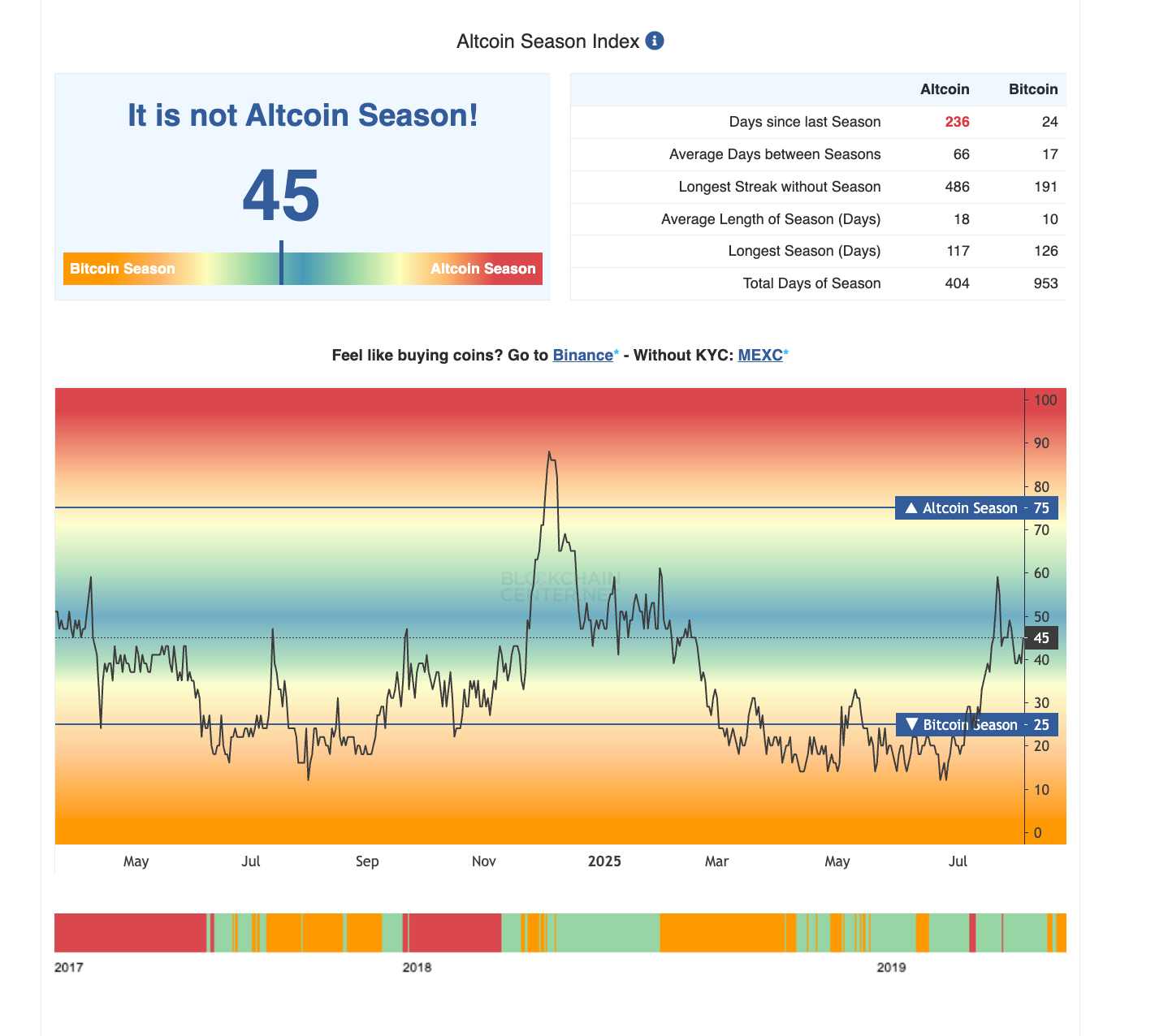
Interest rates sit at 5%, yet Bitcoin is flirting with all-time highs.
Monetary policy has been replaced by fiscal dominance, with stimulus flowing even in economic “good times.”
Markets no longer reflect fundamentals. They reflect liquidity,
Bitcoin’s Insanity: Rational in a Broken World?
Bitcoin doesn’t need a weak economy or rate cuts anymore. In fact, the best macro setup may be no new shocks, just a continued drift in favorable liquidity conditions.
And liquidity is booming:
Global M2 remains elevated, even if topping.
Over $13B in shorts would be liquidated if BTC pumps 10%—indicating dry powder for a parabolic move.
Bitcoin tends to top 525–530 days after halving → That points to late September 2025.
Chart Watch: Minted Macro Breakdown
@MintedMacro offers a crystal-clear roadmap based on historical halving cycles:
Liquidity drives cycles
BTC thrives when M2 grows. Warning: M2 has now double-topped with a lower high.
Timing the top
2013: 525 days post-halving
2017: 530 days
2021: 518 days
➤ 2025 = ~Sept 21st
Projected top zone
$135K–$150K BTC is plausible
But upside may be capped by macro tightening.
Key takeaway
September rally → then a possible liquidity-driven pullback.
With fundamentals distorted and liquidity the dominant force, participants are adapting 👇🧵
Macro Pulse Update 03.08.2025, covering the following topics:
1️⃣ Macro events for the week
2️⃣ Bitcoin Buzz Indicator
3️⃣ Market overview
4️⃣ Key Economic Metrics
5️⃣ India Spotlight
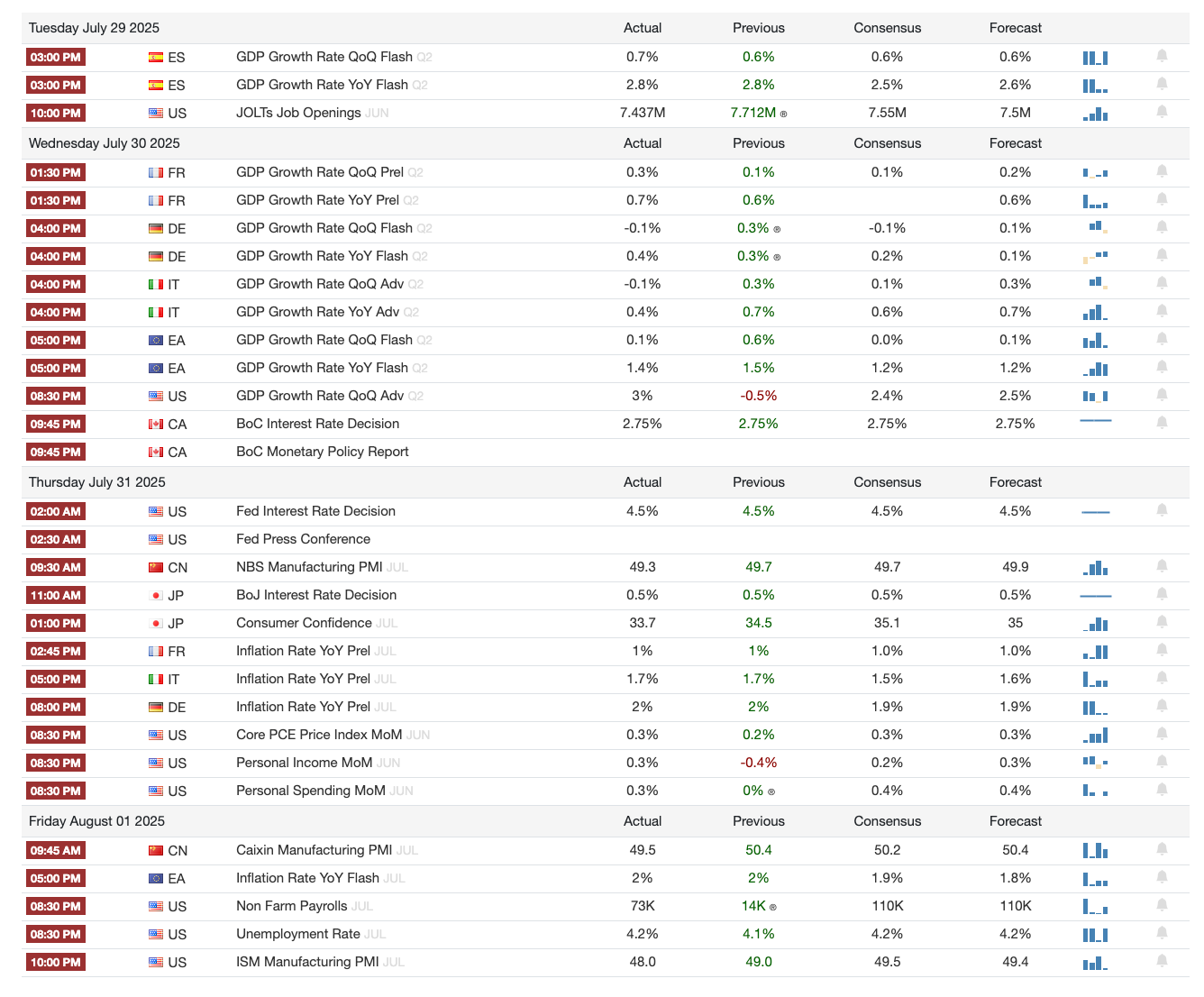
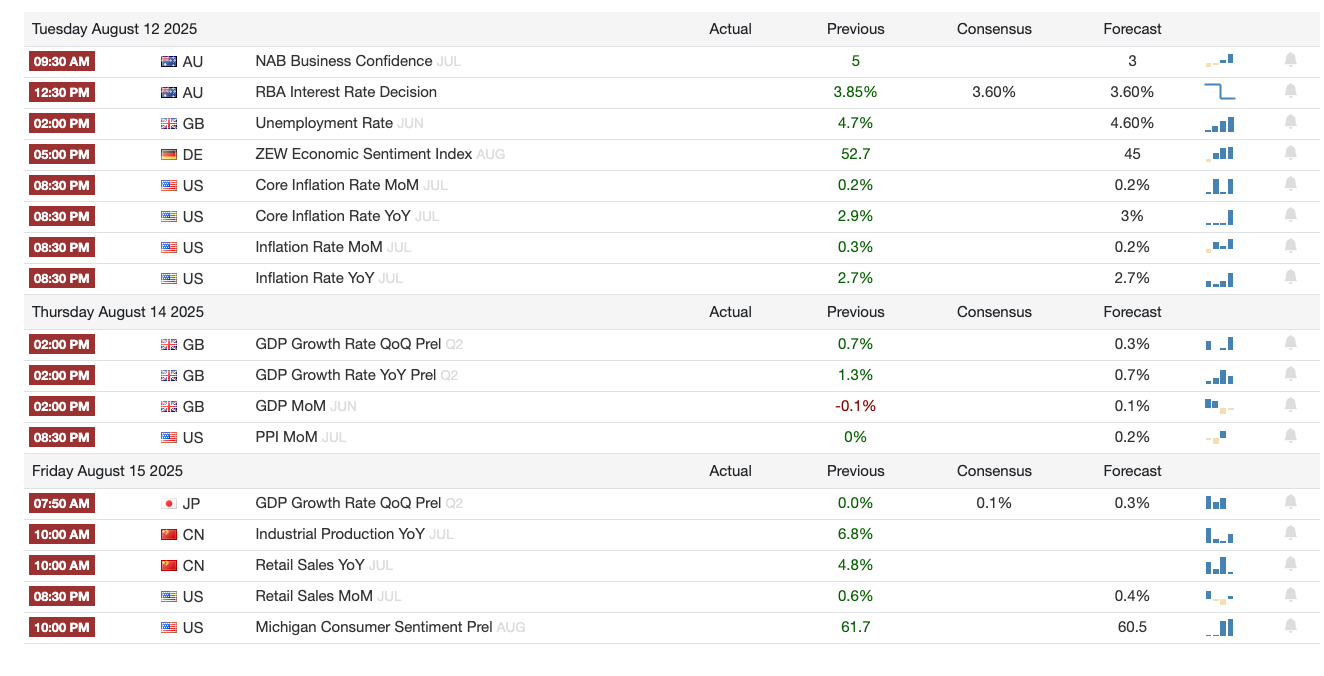
1️⃣ Macro events for the week
Last Week
Next Week
2️⃣ Bitcoin Buzz Indicator
Banking and Regulatory Updates
SEC Launches 'Project Crypto' to Modernize Regulations and Boost U.S. Leadership in Digital Finance
PayPal Launches "Pay with Crypto," Enabling U.S. Businesses to Accept 100 Cryptocurrencies
Visa Expands Stablecoin Settlement Capabilities with New Coins and Blockchains
BNB Hits ATH as Institutional Demand and Corporate Treasuries Fuel Surge
Institutional Investments & Project Development
Tron Inc. Files $1 Billion Securities Statement as TRX's Largest Holder
Strategy Inc. Acquires $739.8M in Bitcoin, Expands Holdings to $43B and Launches Preferred Stock IPO
Tether Reports $4.9B Q2 Profit Amid Strong Demand for Bitcoin and Gold
SharpLink Gaming Acquires $295M in Ethereum, Becomes Second-Largest Holder with 438,017 ETH
Syntetika Hub Launches: Central Hub for Learning, Contribution, and Rewards in Ecosystem
NFT and Digital Collectibles Market
NFT Sales Surge to $574 Million in July, Second-Highest of 2025, Driven by Premium Asset Demand
CryptoPunks Floor Price Reaches $208,000, Hitting Three-Year High Amid ETH Rally
3️⃣ Market overview
U.S. Economy: Signs of a Broader Deceleration
Economic data converged this week to signal a clear and unified message: growth momentum in the U.S. has slowed sharply in the first half of the year.
Consumer behavior is shifting, with households tightening credit card usage despite healthier balance sheets—reflecting a rise in uncertainty rather than optimism.
Housing affordability hit a record low: even with modest price declines, mortgage rates and ownership costs (taxes, insurance, maintenance) have surged. The Atlanta Fed reports that owning a median-priced home now consumes 53% of median income, the highest in history—highlighting a structural barrier to homeownership.
Global Central Banks: Diverging Policy Paths
Policy divergence is emerging: while central banks in Japan, Canada, Brazil, Colombia, and Singapore held rates steady, Chile and South Africa moved ahead with rate cuts of 25 bps, citing disinflation and economic softness.
In the Eurozone, Q2 GDP came in slightly stronger than expected at +0.1% QoQ, but the stability in core inflation at 2.3% YoY suggests ECB caution.
China’s July PMIs softened, indicating that its post-reopening recovery is fading faster than anticipated—potentially dragging down regional demand and supply chains.
U.S. Fed: Data-Dependent Dilemma
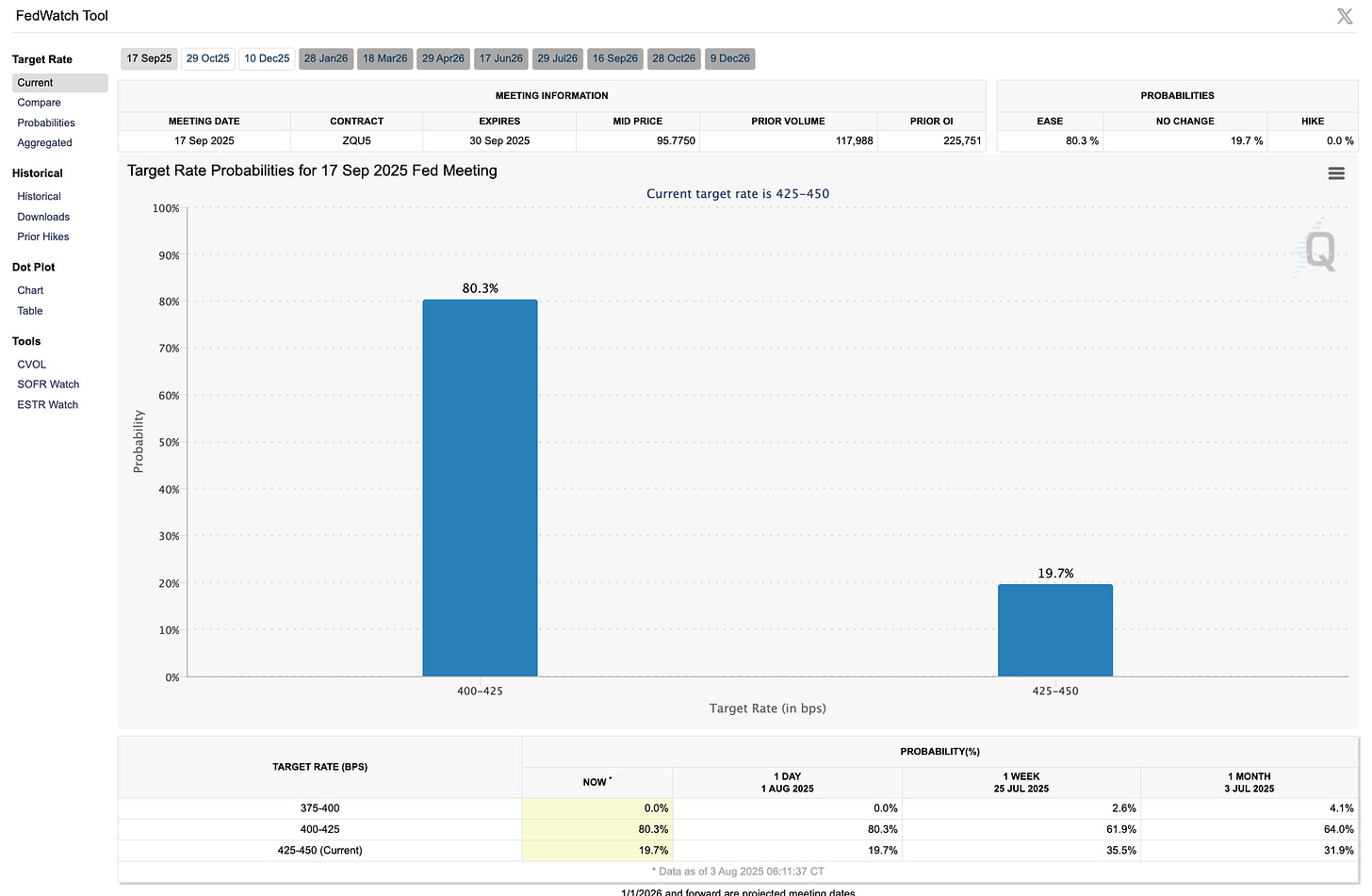
The Fed held rates unchanged at 4.25%–4.50% for the fifth straight meeting, reinforcing its cautious stance amid mixed signals.
September remains a live meeting, but not a guaranteed cut—Fed officials are clearly waiting for clearer evidence from labor markets, inflation, and consumer data before making the next move.
The outlook hinges on how deep the slowdown runs and whether inflation continues to ease without tipping the economy into recession.
4️⃣ Key Economic Metrics
US Japan Deal
New Tariff Agreement: Lower Than Threatened, But Still High
The U.S. announced a 15% tariff on all Japanese imports, up from 10% and sharply higher than the 2.5% at the start of the year.
Automobiles and parts, previously at a 27.5% tariff, will now be aligned at 15%, leading to a surge in Japanese auto stocks and equities.
Inflation Risk from Higher Import Prices
Despite avoiding the extreme 25% rate, a 15% tariff still raises consumer prices on Japanese goods, adding pressure on inflation and reducing U.S. household purchasing power.
The broader trade policy shift could further elevate import costs across other regions.
Japan’s $550B Investment Pledge: Unclear Terms
Trump claimed Japan will invest $550B into the U.S., with 90% of profits going to the U.S.—calling it a “signing bonus.”
However, Japan’s negotiators argue the figure is a ceiling, not a guaranteed amount, and expect the U.S. to share risk and financing.
The lack of a written agreement raises questions about enforceability and opens the door for future disputes.
U.S. Manufacturing Push Faces Labor Constraints
The deal aims to shift more manufacturing activity into the U.S., but with labor shortages and tight immigration, it’s unclear how this production will be staffed.
This contradiction weakens the strategy to reduce the trade deficit through reshoring.
Auto Industry Backlash: Uneven Playing Field
U.S. automakers face higher costs than Japanese importers due to:
25% tariffs on imported parts.
50% tariffs on imported steel and aluminum.
Complicated rebate processes under NAFTA/USMCA.
Industry leaders warn that the deal favors Japan over U.S. manufacturers and workers, with fears it may set a precedent for future trade deals.
Deal in Doubt: More a Handshake than a Contract
No formal treaty was signed; both parties are already disputing the interpretation.
Raises broader concerns about the U.S.’s reliance on non-binding trade commitments, which could erode trust and stability in future negotiations.
Jobs Market
New Grads Face an Unprecedented Hiring Slump
The unemployment rate for recent college graduates is now at a decade-high—and just one percentage point lower than for all young workers, an unusually narrow gap.
Historically, college grads have enjoyed much stronger job prospects compared to their peers. This convergence is a red flag for white-collar employment trends.
AI Is Not the Primary Culprit—Yet
While generative AI is blamed for killing off entry-level jobs, its impact remains limited to specific sectors (e.g., tech).
Broader implementation is still too sparse to explain the widespread weakness in graduate hiring.
Policy Uncertainty Is Freezing the Market
Uncertainty around trade policy, Fed interest rate direction, and immigration restrictions is likely deterring companies from hiring, especially for skilled roles.
This climate of uncertainty also affects worker behavior—quit rates are low, reflecting reluctance to job-switch in an unstable market.
Reduced quits = fewer openings, leading to slower labor market churn.
The Skilled Worker Shortage Is Easing
The long-standing shortage of college-educated workers—once a key driver of high wage premiums—is diminishing.
As more workers enter the skilled labor pool, the wage premium is flattening or falling, which could further dampen job creation in traditionally high-growth sectors.
5️⃣ India Spotlight🔴
UK–India Trade Deal: A Major Non-U.S. Pivot
UK and India finalize a landmark trade deal that slashes tariffs on over 90% of UK exports to India.
The UK expects a 60% increase in exports to India by 2040, driven by improved access to a fast-growing market.
Big Win in Autos
India cuts auto import tariffs from 100% to 10%, a dramatic reduction that could transform the car market.
However, a quota limits total imports, capping the immediate commercial upside for UK automakers.
India Gains Quietly but Significantly
While headlines focus on UK export gains, India benefits most from its own tariff cuts:
Lower prices for consumers
Increased domestic competition
Stronger global competitiveness for Indian firms
These structural gains may enhance India’s long-term export capacity and productivity.
Half of Indian Exports to UK Now Tariff-Free
Previously facing 4%–16% tariffs, about 50% of Indian exports to the UK will now enter duty-free, helping Indian exporters in textiles, pharmaceuticals, and food products.
Strategic Trade Realignment
The deal reflects a broader global trend: as U.S. tariffs disrupt existing trade patterns, countries are diversifying partnerships.
India is actively pursuing trade liberalization with the EU, ASEAN, and even the U.S., positioning itself as a pivotal player in the post-globalization reset.